This scenario reminds me of an emerging virtual world named Second Life. Second Life is a virtual world developed by Linden Lab and was launched in 2003. The purpose of Second Life is to create a virtual avatar that will enable a person to free themselves from their personal world. According to Second Life, the virtual world is a “place to connect, a place to shop, a place to work, a place to love, a place to explore, a place to be different, be yourself, free yourself, free your mind, change your mind, change your look, love your look, and love your life.” Second Life is a perfect example of using the virtual world as a way of escaping one’s environment. The virtual character liberates the users from reprisals and allows the users to say and do things that they might not have.
Tuesday, October 27, 2009
Virtual World
This scenario reminds me of an emerging virtual world named Second Life. Second Life is a virtual world developed by Linden Lab and was launched in 2003. The purpose of Second Life is to create a virtual avatar that will enable a person to free themselves from their personal world. According to Second Life, the virtual world is a “place to connect, a place to shop, a place to work, a place to love, a place to explore, a place to be different, be yourself, free yourself, free your mind, change your mind, change your look, love your look, and love your life.” Second Life is a perfect example of using the virtual world as a way of escaping one’s environment. The virtual character liberates the users from reprisals and allows the users to say and do things that they might not have.
The Immoral world of Virtual Reality
I think that it is an important when dealing with virtual reality to speak about the morality of what goes on. Is mutilating and killing someone in a virtual world an okay thing to do because you arent physically harming someone? Or does this ability to commit virtual crimes foster the ability for one to commit these crimes in the physical world? Should there be regulations for committing especially heinous crimes in virtual reality? Many questions like these are being dealt with today, but who knows if a concrete conclusion will ever come, due to the broadness and unpredictability of the cyberworld.
Welcome to Cyberspace
 I like these pictures because they create words that essentially come to mind when we think cyberspace. The vast communication patterns that can be achieved in cyberspace are represented above, while below represents the matrix of virtual infrastructure.
I like these pictures because they create words that essentially come to mind when we think cyberspace. The vast communication patterns that can be achieved in cyberspace are represented above, while below represents the matrix of virtual infrastructure.The Point to PowerPoint?
“Electronic technology offers two distinct sets of tools for presentation and representation: tools for writing, and tools for visualization and sensory presentation. The computer and attendant technologies call forth both a new writing space and new perceptual space. Each of these new spaces in turn fosters a different construction of self” (130).
I found this section to be particularly through provoking when applied to the ideals behind the creation of Microsoft Office. Most, if not all of us, use Microsoft Office. Office comes with such programs as Word, PowerPoint, and Excel. However, when creating either a word document, a chart, or a PowerPoint, we are creating a way to communicate with others. But, though these ways of communication, we are able to personalize the overall appearance, which can change the overall message.
Think about it: if you are shown a PowerPoint presentation in class, which one are you more likely to pay attention to? The presentation that is in purely black and white, Time New Roman, or the presentation with slide designs, fancy fonts and appealing transitions? The way that we “design” and personalize our message can change the overall impact it has on our audiences.
There are numerous ways we use technologies to help define ourselves. Just from reading this post, can you guess my favorite color?
Military and Cyberspace
"ON OCTOBER 1, just beyond the Beltway inside Fort Meade, a four-star general became the first head of America’s new Cyber Command. Subordinate to General Keith Alexander are the Tenth Fleet and the Twenty-Fourth Air Force. The fleet has no ships, and the air-force unit has neither aircraft nor missiles. Their weapons are ones and zeroes. Their battlefield is cyberspace.
The mission of Cyber Command is to protect the U.S. military’s networks and to be ready to launch offensive cyber attacks on a potential enemy. Those offensive cyber attacks have the potential to reach out from cyberspace into the physical dimension, causing giant electrical generators to shred themselves, trains to derail, high-tension power-transmission lines to burn, gas pipelines to explode, aircraft to crash, weapons to malfunction, funds to disappear and enemy units to walk into ambushes. Welcome to warfare in the twenty-first century."
This is the full article http://www.nationalinterest.org/Article.aspx?id=22340
Virtual Reality Simulators

Flaming and Cyberspace
These flames are found all over the internet on blogs, discussion boards, emails, chat rooms, and IMs. When I used to go into chat rooms and talk more frequently online, I would constantly see these flames posted everywhere. Over the internet, people can put on a mask that they would not usually wear. People have a confidence when not put face to face with a person; they say things they would usually not. Flames turned into the newer phenomenon of "cyberbullying." Parents now are encouraged to monitor their children's interaction over the internet not only for questionable websites, but also for bullying. There is a lot of information on the web about this subject, but I found this video to be interesting:
THE PHILOSOPHICAL REALM
Cyberspace, Motion & The Self
Monday, October 26, 2009
The Virutal Classroom
"Imagine a classroom equally available to anyone, anywhere in the world--or, for that matter, off of the world--with a personal computer and connection to a phone system. Think of a classroom whose discussions, proceeding asynchronously, went on continuously, 24 hours a day, with no absolute limitation on how many people could participate at any one time. And picture yourself with access to a library comprised of papers that could be read by thousands of people, all at once, and yet these texts would still be there for you whenever you wished (p. 216)."Our Intro to New Media class is a genuine testament to this statement. By use of social media and social networking (blogging, Google groups, YouTube, etc.), every student in the class has resources available to them at any hour of the day and can instantly read and comment what other students have written, by means of our blog. However, the class blog is not limited to only students in our class. Thousands of people (hypothetically speaking...) can read our blog, question our thoughts, use an entry as a source for their own means, and even comment on our work. This type of interactive learning could never have been achieved without a "virtual classroom" or the boom of social networking/social media over the past few years. Although the blog has only been subject to comments and interaction from class-members, for now, the basic principle behind this type of interactive, digital learning environment is still exemplified. Discussion can potentially go on 24 hours a day and there is literally no limit to the amount of people who participate or add to it.
Communication and Cyberspace also brings up the advantage of earning a degree online. The idea of earning college credits online surfaced with the New York Institute of Technology, offering a few online courses for a modest tuition, in the mid 1980s and only flourished from then on. "The process of online education works like email, except rather than one person communication to another or a group of people, many people communicate to many, with the website or external computer system playing the crucial role of keeping track of who in the group has read who else's messages (p. 217-18)." The important component of learning, usually lacking from the traditional classroom setting, is students interactively learning from other students. One of the major advantages of online learning is the ability to actually learn from what other students have read in an interactive way. In a traditional classroom, professors tend to "inject or spoonfeed information into passive student minds (p. 222)."
Although there are downsides to virtual learning, the advantages prove to trump them. Learning by means of a digital medium opens up vast amounts of opportunity for those with time constraints, computer or internet based classes, or the desire to gain a degree while working full time. As explained before, even a traditional class setting can benefit from putting an aspect of the course material online, in an interactive format.
I've included this chart, which does a great job of visualizing the advantages of online learning.
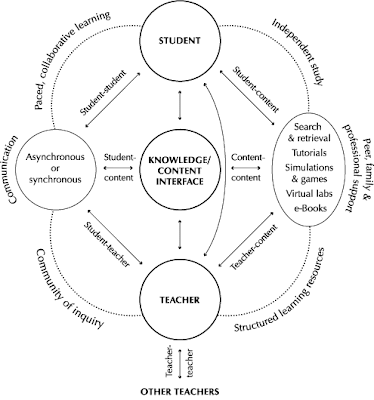
Will people blur the lines between Virtual Reality and Reality?
Tuesday, October 20, 2009
Tweeting Cyberspace
Six Degrees of Separation
Hyperlink
Neil Postman
Cyberspace
Virtual reality, though it has slowed down in progress, has some really cool aspects to it. The army frequently creates simulators to imagine what iit would be like in battle. Drawing from this technology, consumers have been exposed to virtual reality through all sorts of different things. Disney world had this exhibit where you could ride a "virtual space mountain": (skip to about 1:30 for the video)
Medical Telepresence & Robotic surgery
Cyberspace
Cyberspace: a virtual world
Tuesday, October 6, 2009
Digital and Analog
Privacy in the Digital World
Unlike computers, humans perceive information in analog. We capture auditory and visual signals as a continuous stream. Digital devices, on the other hand, estimate this information using ones and zeros. The rate of this estimation, called the "sampling rate," combined with how much information is included in each sample (the bit depth), determines how accurate the digital estimation is.
This video actually ends up being an ad for SafehouseExplorer but the concept of the video is really important. In this "digital age" our privacy is at an increased risk. Many of us have our whole lives on our computers, online, and on our cell phones; Our whole worlds saved into binary code. Websites track our use and save data, you lose a usb drive, you lose all of your personal information. Thanks digital world, where did our privacy go?!
Digital Information
The Digital World
What's the Difference Between Analog and Digital?
This is a diagram of an analog wave:
 One of the disadvantages to an analog signal is its susceptibility to be interfered with by noise. Because analog signals are not easily compressed, they are more likely to be warped by unwanted noise.
One of the disadvantages to an analog signal is its susceptibility to be interfered with by noise. Because analog signals are not easily compressed, they are more likely to be warped by unwanted noise.In digital technology, the analog wave is sampled at some interval, and then turned into numbers that are stored in a digital device. Computers do this by converting the signal into a strain of 1's and 0's. A cd player is an example of a digital technology, while an audio cassette player would be an example of an analog one.
Digital recording has many advantages over analog. Primarily, it produces a much warmer, richer, and more natural sound than analog recording. The reason for this is demonstrated in the following picture:
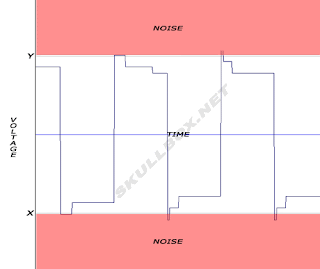 As one can see, because digital signals can be compressed and their waves can only reach a certain height, they are not very susceptible to interference from noise. As a result, the waves maintain their original form and are easily and accurately interpreted by a computer.
As one can see, because digital signals can be compressed and their waves can only reach a certain height, they are not very susceptible to interference from noise. As a result, the waves maintain their original form and are easily and accurately interpreted by a computer.
Digital vs. Analog in Recording and A Recent Digital Event
Digital Manipulation
One of the most common comparisons made between digital and analog is with music recordings. At what point does a digital file cease to be a recording, and instead become a programmed performance in its own right? Lance Strate proposed this question in an earlier post and it speaks to a lot of controversy surrounding digital and analog forms of recording. Some musicians prefer analog recordings because the sound you hear is as close to being in the same room as the artist as possible without actually being there. However, modern recording artists tend to take full advantage of digital recording capabilities. Digital recordings can be converted, enhanced and manipulated on a computer to give you the final product. Take the newly popular “auto-tune” digital feature used by popular artists like Kanye West, and originally Cher in her song “Believe,” to produce a synthesized, digitally “perfect” vocal tone. Auto-tune uses a voice encoder to correct pitch in vocal and instrumental performances. It is used to disguise inaccuracies and mistakes, and has allowed many artists to produce more precisely tuned recordings (Wikipedia). Although the music we hear today on the radio is widely popular, could we actually call them “recordings?” What are the justifications between authentic audio content and an enhanced, auto-tuned “performance?”
There is no answer to this argument. Consumers in our modern society take tweaked and manipulated audio files to be forms of entertainment and have become widely popular. Digital technology has allowed for numerous advancements in music and the outcome of such is a subjective matter. Some will see it as taking away from the true talent that many musicians possess and others see it as the future and pure-genius.
Source: pcmag.com, techmind.org, wikipedia.org
Monday, October 5, 2009
Digital definition
Digital Language & Communication
DIGITAL
According to PCMAG digital “means perfect copies, the 0s and 1s of digital data mean more than just on and off. They mean perfect copying. When information, music, voice and video are turned into binary digital form, they can be electronically manipulated, preserved and regenerated perfectly at high speed. The millionth copy of a computer file is exactly the same as the original. While this continually drives the software and content publishers crazy protecting their copyrights, it is nevertheless a major advantage of digital processing.”
Nearly everything has become or is becoming digital. From digital video discs (DVD) to digital photography, we are surrounded by everything that is digital. We are drawn to everything digital because it brings many benefits for both consumers and firms. In addition, virtually everything is transitioning towards the internet and adapting to the rapidly changing world of media. According to techmind.org, “when compared to analog records or cassette tape, the CD has demonstrated greater dynamic range (which means no hiss during quiet parts of the music), very good and flat frequency response (so the sound is crisp), and the format is notably resilient to dust, dirt and scratches.” This is even more true for compressed MP3’s.
However, the digital world has not brought enthusiasm to everyone. Stephen Lacy, Professor at Michigan State University states that the “digital distribution of information has created concerns about the future of news organizations. Observers have speculated on how the Internet has and will change journalism, with almost as many different conclusions as there are speculators. These concerns have caused journalism educators around the country to reevaluate how they teach journalism.”
The future for digital technology is uncertain, but what is certain is that we will continue to accept, entrust and rely on digital technologies.
digital takeover?
Although as a culture it seems like digital technologies are preferred at this point, we do have to give some credit to analog technologies. Without analog technologies, we (or our parents!) would not have been able to listen to the music that defined their generation. Analog technologies were used for vinyl records, 8-tracks, and even cassettes. In a way, I almost prefer analog technologies as a way to define a true artist. Although we have many great talents of our generation, digital technologies for CDs and MP3s help “clean up” tracks that artists create; they’re “digitally” remastered. Do you think this takes away from the artist’s credibility as a true talent, if their “talent” can be digitally restored and edited?
However, digital technologies sometimes rely on analog technologies to exist. For example, “when an analog waveform like music is recorded with a digital recorder, the music is sampled several thousand times per second. For a CD-quality recording, the average sampling rate is 44,000 times per second. That’s 44,000 numbers stored for each second of music. The higher the sampling rate, the more accurate the recording” (wisegeek.com).
Here’s a really interesting, real life example on the differences between analog and digital when it comes to artists recording and using modern technologies
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rrJBEmz5teA
I just have to wonder how much longer analog technologies will still be used in our world of digital media.
Sunday, October 4, 2009
DIGITAL VS ANALOG
As a technology, analog is the process of taking an audio or video signal (in most cases, the human voice) and translating it into electronic pulses. Digital on the other hand is breaking the signal into a binary format where the audio or video data is represented by a series of "1"s and "0"s. Simple enough when it's the device—analog or digital phone, fax, modem, or likewise—that does all the converting for you.
The newer of the two, digital technology breaks your voice (or television) signal into binary code—a series of 1s and 0s—transfers it to the other end where another device (phone, modem or TV) takes all the numbers and reassembles them into the original signal. The beauty of digital is that it knows what it should be when it reaches the end of the transmission. That way, it can correct any errors that may have occurred in the data transfer. What does all that mean to you? Clarity. In most cases, you'll get distortion-free conversations and clearer TV pictures.
The word DIGITAL describes any system based on discontinuous data or events. The important word here is discontinuous, which means not continuous or having breaks. The opposite of digital is analog.
ANALOG processes information more or less in a continuous stream. The difference can be easily seen in a clock. An analog clock is one with hands that move around the clock continuously producing a stream of time. Any minute and any fraction of a minute can be represented. For instance, you could look at an analog clock and say with some degree of accuracy that it is one and one half minutes past one o'clock. You could see that the minute hand was half way between one and two minutes. The average digital clock, which shows the time by flashing the hour and the minute, produces distinct minutes but cannot represent a half of a minute or a quarter of a minute. The digital clock will show that it is one minute past one or two minutes past one. You cannot tell from looking at the clock if it is one and one half minutes past one or one and a quarter minutes past one.
From the above description, you may surmise that analog is more detailed than digital, but that assumption would be incorrect. Although the normal digital clock will show only minutes, a more detailed digital clock could show fractions of minutes – even a thousandth or millionth of a second, something that an analog clock could not do as accurately. Digital equipment can accurately produce minute details. In addition, digital processing is important because a computer or other digital piece of equipment can store and manipulate digital signals quickly and easily. In addition, digital signals can be converted to analog signals to create a very high quality reproduction.
http://telecom.hellodirect.com/docs/Tutorials/AnalogVsDigital.1.051501.asp
www.dictionary.com
http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/question7.htm
http://www.cellphonecarriers.com/compare-digital-analog.html
Digital and Analog Technology
Analog capabilities has been around for many decades, while digital is a newer ability. Among the disadvantages of analog are the limitations of the amount of data it can carry. Analog technology can only handle so much information at a time until it is overwhelmed. The new digital technology however, in breaking up sound and video and placing it into binary code, can carry more data. Disadvantages of digital are that since the technology is consistantly encoding and decoding, the quality of the end message isn't as clear as the analog version since it has been dismantled and put back together when recieved.
In today's world, we are consistantly hearing of new digital availabilities. Digital satellite television, or digital phones service. Having not really known what the big difference is, the way they make it sound in commercials is that digital is far superior to analog. And while it may be better, the disadvantage of bad quality is a concerning.
Friday, October 2, 2009
Digital vs. Analog
But! According to the website, digital is technology that transmits data in terms of positive or negative. These polarities are represented by a string of 1's and 0's, which goes back to the difference between bits and bytes. Each of these individual digits is a bit, but a string of them together used to convey information is a byte.
Analog is the older medium for processing information. Instead of the string of information conveyed in 1's and 0's, analog sends information by electric signals that have different frequencies and amplitudes.
Digital is the technology used in satellite communication, new cell phones, and fiber optics. The change over to strictly digital TV happened June 12th, but was supposed to happen much earlier. The government was handing out coupons in order to aid people who wanted to purchase a digital box. If a person used to use an antennae on top of his house to get tv, he would be using analog signals, while anyone watching FiOs tv is in the new era of digital technology.
Thursday, October 1, 2009
A Glance at Digital Divide
- Analog-Analog systems are very tolerant to noise, make good use of bandwidth, and are easy to manipulate mathematically. However, analog signals require hardware receivers and transmitters that are designed to perfectly fit the particular transmission. If you are working on a new system, and you decide to change your analog signal, you need to completely change your transmitters and receivers.
- Digital-Digital signals are intolerant to noise, and digital signals can be completely corrupted in the presence of excess noise. In digital signals, noise could cause a 1 to be interpreted as a 0 and vice versa, which makes the received data different than the original data. Imagine if the army transmitted a position coordinate to a missile digitally, and a single bit was received in error? This single bit error could cause a missile to miss its target by miles. Luckily, there are systems in place to prevent this sort of scenario, such as checksums and CRCs, which tell the receiver when a bit has been corrupted and ask the transmitter to resend the data. The primary benefit of digital signals is that they can be handled by simple, standardized receivers and transmitters, and the signal can be then dealt with in software (which is comparatively cheap to change).
